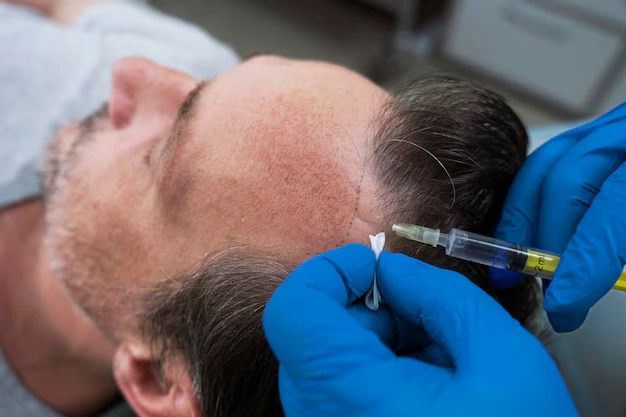
Hormonal imbalances can play a significant role in hair loss, affecting both the progression of thinning and the results of hair restoration procedures. Understanding how hormones interact with hair follicles is essential for patients considering a hair transplant, ensuring realistic expectations and long-term success.
How Hormones Affect Hair Growth
Hormones such as dihydrotestosterone (DHT), thyroid hormones, and sex hormones like estrogen and testosterone directly influence hair follicle health. Excess DHT, for instance, can shrink follicles and accelerate male pattern baldness, while thyroid imbalances may trigger diffuse shedding in both men and women. Recognizing these underlying factors helps surgeons plan effective interventions tailored to individual patients.
Timing a Hair Transplant with Hormonal Considerations
For patients with ongoing hormonal imbalances, timing a hair transplant appropriately is crucial. Surgeons often recommend stabilizing hormone levels before surgery to ensure that transplanted follicles are not exposed to the same conditions that caused the original hair loss. This approach enhances graft survival and reduces the risk of future thinning in both transplanted and native hair.
Assessing Hair Loss Causes
Not all hair loss is suitable for transplantation. Patients experiencing active shedding due to hormonal fluctuations may require medical treatment first. Blood tests and consultations with endocrinologists or dermatologists can identify the exact cause, allowing a combined approach that addresses hormonal issues while planning for surgical restoration. This ensures better predictability and long-term outcomes.
Post-Transplant Considerations
After a hair transplant, maintaining stable hormone levels is essential for preserving grafts and preventing further loss. Patients may need ongoing medications or lifestyle adjustments to regulate hormones, depending on the underlying condition. Regular follow-ups with both the hair restoration clinic and a healthcare provider help monitor hair health and adjust treatment strategies as needed.
Combining Medical and Surgical Solutions
In many cases, combining hormonal treatment with hair transplantation yields the best results. For example, DHT blockers, thyroid therapy, or hormone replacement can stabilize hair loss, allowing transplanted follicles to thrive. A tailored plan that addresses both medical and surgical aspects provides a comprehensive approach for patients affected by hormonal imbalances.
Final Thoughts
Hormonal imbalances significantly influence hair loss and hair transplant outcomes. Understanding the role of hormones, timing the procedure appropriately, and combining medical management with surgery ensures better graft survival and long-term hair health. Patients who address hormonal factors proactively are more likely to achieve natural, lasting results.
Dealing with hair loss due to hormonal imbalance? Contact Badge Health today for expert guidance, personalized treatment plans, and strategies to maximize your hair transplant results while managing hormonal health effectively.